https://ksw0723.tistory.com/193
A* 알고리즘 구현해보기 (1) - 이동 불가 노드와 이동 가능 노드 구별하기
오늘은 A* 알고리즘을 구현해보려고 한다. 참고 블로그 및 사이트는 https://m.blog.naver.com/pkh879/221735054051 Unity - A* 알고리즘 구현하기 Part 2 이제부터는 실제로 Unity로 A* 알고리즘을 구현해보겠습니
ksw0723.tistory.com
지난 글에 이어서
이번에는 출발 지점에서 목표 지점 까지의 경로(Path)를 구하고
그 경로를 눈으로 직접 살펴보려고 한다.
일단 지난번의 스크립트를 수정하자.
using UnityEngine;
public class Node
{
public bool isWalkAble;
public Vector2 worldPos; // 2D
public int gridX;
public int gridY;
public int gCost;
public int hCost;
public Node parentNode;
public Node(bool walkable, Vector2 worldPosition, int nGridX, int nGridY)
{
isWalkAble = walkable;
worldPos = worldPosition;
gridX = nGridX;
gridY = nGridY;
}
public int fCost
{
get { return gCost + hCost; }
}
}Node.cs
Node 클래스에 F,G,H cost 변수와
Node의 X와 Y 변수를 추가했다.
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Unity.Mathematics;
using UnityEngine;
public class Grid : MonoBehaviour
{
public LayerMask unwalkableMask;
public Vector2 gridWorldSize;
public float nodeRadius;
public List<Node> path;
Node[,] grid;
float nodeDiameter;
int gridSizeX, gridSizeY;
void Start()
{
nodeDiameter = nodeRadius * 2;
gridSizeX = Mathf.RoundToInt(gridWorldSize.x / nodeDiameter); // 가로길이
gridSizeY = Mathf.RoundToInt(gridWorldSize.y / nodeDiameter); // 세로길이
CreateGrid();
}
void CreateGrid()
{
grid = new Node[gridSizeX, gridSizeY];
Vector2 worldBottomLeft = (Vector2)transform.position - Vector2.right * gridWorldSize.x / 2 - Vector2.up * gridWorldSize.y / 2;
for (int x = 0; x < gridSizeX; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < gridSizeY; y++)
{
Vector2 worldPoint = worldBottomLeft + Vector2.right * (x * nodeDiameter + nodeRadius) + Vector2.up * (y * nodeDiameter + nodeRadius);
bool walkable = !(Physics2D.OverlapCircle(worldPoint, nodeRadius, unwalkableMask));
grid[x, y] = new Node(walkable, worldPoint,x,y);
}
}
}
// 노드의 주변 노드(8방면)를 찾는 메서드
public List<Node> GetNeighbours(Node node)
{
List<Node> neighbours = new List<Node>();
for(int x = -1; x<= 1; x++){
for(int y = -1; y <= 1; y++)
{
if(x == 0 && y ==0) continue; // 자기 자신인 경우는 스킵
int checkX = node.gridX + x;
int checkY = node.gridY + y;
// X, Y의 값이 Grid 범위 안에 있을 경우
if(checkX >= 0 && checkX < gridSizeX && checkY >= 0 && checkY < gridSizeY)
{
neighbours.Add(grid[checkX, checkY]);
}
}
}
return neighbours;
}
// 유니티의 WorldPosition로 부터 그리드상의 노드를 찾는 메서드
public Node GetNodeFromWorldPoint(Vector2 worldPosition)
{
float percentX = (worldPosition.x + gridWorldSize.x / 2) / gridWorldSize.x;
float percentY = (worldPosition.y + gridWorldSize.y / 2) / gridWorldSize.y;
int x = Mathf.RoundToInt((gridSizeX - 1) * percentX);
int y = Mathf.RoundToInt((gridSizeY - 1) * percentY);
return grid[x, y];
}
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(transform.position, new Vector3(gridWorldSize.x, gridWorldSize.y, 1));
if (grid != null)
{
foreach (Node n in grid)
{
Gizmos.color = (n.isWalkAble ? Color.white : Color.red);
// 탐색된 Path의 노드 표시
if (path != null)
if (path.Contains(n))
Gizmos.color = Color.black;
Gizmos.DrawCube(n.worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - .1f));
}
}
}
}Grid.cs
Node 생성자 변경으로 인한 매개변수 추가와
GetNodeFromWorldPoint, GetNeighbours 메서드 추가
GetNodeFromWorldPoint
씬에 있는 오브젝트와, 목표 오브젝트가 있는 노드를 얻기 위한 메서드
GetNeighbours
열린 목록(List)에 추가하기 위한 메서드
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Pathfinding : MonoBehaviour
{
Grid grid;
[SerializeField] Transform startGO; // 시작 위치를 나타내는 Transform
private void Awake()
{
grid = GetComponent<Grid>();
}
private void Update()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(1)) // 마우스 우클릭 감지
{
Vector2 mousePosition = Camera.main.ScreenToWorldPoint(Input.mousePosition);
FindPath(startGO.position, mousePosition);
}
}
void FindPath(Vector2 startPos, Vector2 targetPos)
{
Node startNode = grid.GetNodeFromWorldPoint(startPos);
Node targetNode = grid.GetNodeFromWorldPoint(targetPos);
List<Node> openList = new List<Node>();
HashSet<Node> closeList = new HashSet<Node>();
openList.Add(startNode);
while (openList.Count > 0)
{
Node currentNode = openList[0];
// 열린 목록에 F cost가 가장 작은 노드를 찾는다. 만약 F cost가 같다면 H cost가 작은 노드를 찾는다.
for (int i = 1; i < openList.Count; i++)
{
if (openList[i].fCost < currentNode.fCost || (openList[i].fCost == currentNode.fCost && openList[i].hCost < currentNode.hCost))
{
currentNode = openList[i];
}
}
// 탐색된 노드는 열린목록에서 제거하고 닫힌 목록에 추가
openList.Remove(currentNode);
closeList.Add(currentNode);
// 탐색된 노드가 목표 노드라면 탐색 종료
if (currentNode == targetNode)
{
RetracePath(startNode, targetNode);
return;
}
foreach (Node neighbour in grid.GetNeighbours(currentNode))
{
// 이동불가 노드이거나 닫힌 목록에 있는 경우는 스킵
if (!neighbour.isWalkAble || closeList.Contains(neighbour)) continue;
// 이웃 노드들의 G cost와 H cost를 계산하여 열린 목록에 추가한다.
int newCostToNeighbour = currentNode.gCost + GetDistanceCost(currentNode, neighbour);
if (newCostToNeighbour < neighbour.gCost || !openList.Contains(neighbour))
{
neighbour.gCost = newCostToNeighbour;
neighbour.hCost = GetDistanceCost(neighbour, targetNode);
neighbour.parentNode = currentNode;
if (!openList.Contains(neighbour)) openList.Add(neighbour);
}
}
}
}
// 탐색종료 후 최종 노드의 ParentNode를 추적하며 리스트에 담는다.
void RetracePath(Node startNode, Node endNode)
{
List<Node> path = new List<Node>();
Node currentNode = endNode;
while (currentNode != startNode)
{
path.Add(currentNode);
currentNode = currentNode.parentNode;
}
path.Reverse();
grid.path = path;
}
// 두 노드간의 거리로 Cost를 계산한다.
int GetDistanceCost(Node nodeA, Node nodeB)
{
int distX = Mathf.Abs(nodeA.gridX - nodeB.gridX);
int distY = Mathf.Abs(nodeA.gridY - nodeB.gridY);
if (distX > distY) return 14 * distY + 10 * (distX - distY);
return 14 * distX + 10 * (distY - distX);
}
}Pathfinding.cs
A* 알고리즘으로 열린 목록과 닫힌 목록을 리스트로 생성해주고,
현재 위치를 열린 목록에 담아준다.
그리고 열린 목록 중 F cost가 가장 적은 노드를 찾아 탐색한다.
여기서 비용 계산은
GetDistanceCost 메서드로 진행하는데,
두 노드 간의 x축 길이(distX)와 y축 길이(distY)를 구해서
x축 이동, y축이동, 대각선 이동에 따른 cost를 계산한다.

그리고 만약 F cost가 같다면, H cost가 적은 노드로 탐색을 한다.
그 후, 탐색된 노드의 이웃노드를 열린 목록에 추가하고,
이웃 노드들의 Parent를 탐색된 노드로 지정한다.
이하 최종 노드가 탐색 될 때 까지 반복 실행.
최종 노드까지 탐색되면 종료하고
RetracePath 메서드를 통해 최종 노드의 ParentNode를 따라가면서 Path가 완성된다.
**Path.Reverse()
최종 노드부터 다시 거꾸로 가기 때문에 다시 Reverse 해주면 순차적으로 path가 된다.
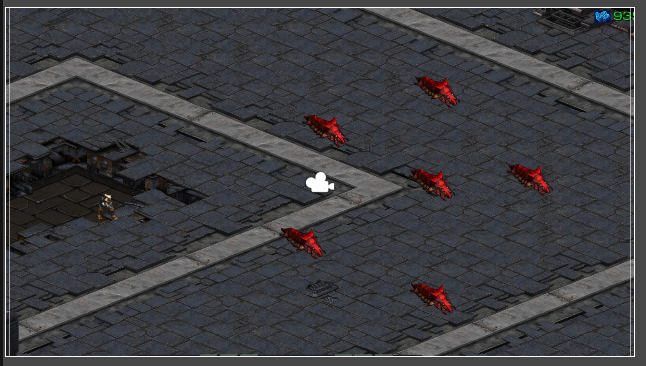
씬으로 돌아와서
시작점과 벽(또는 장애물)을 세팅해주자.
왼쪽의 Zillot이 우리가 움직일 시작점,
Larva들이 피해서 갈 장애물이다.
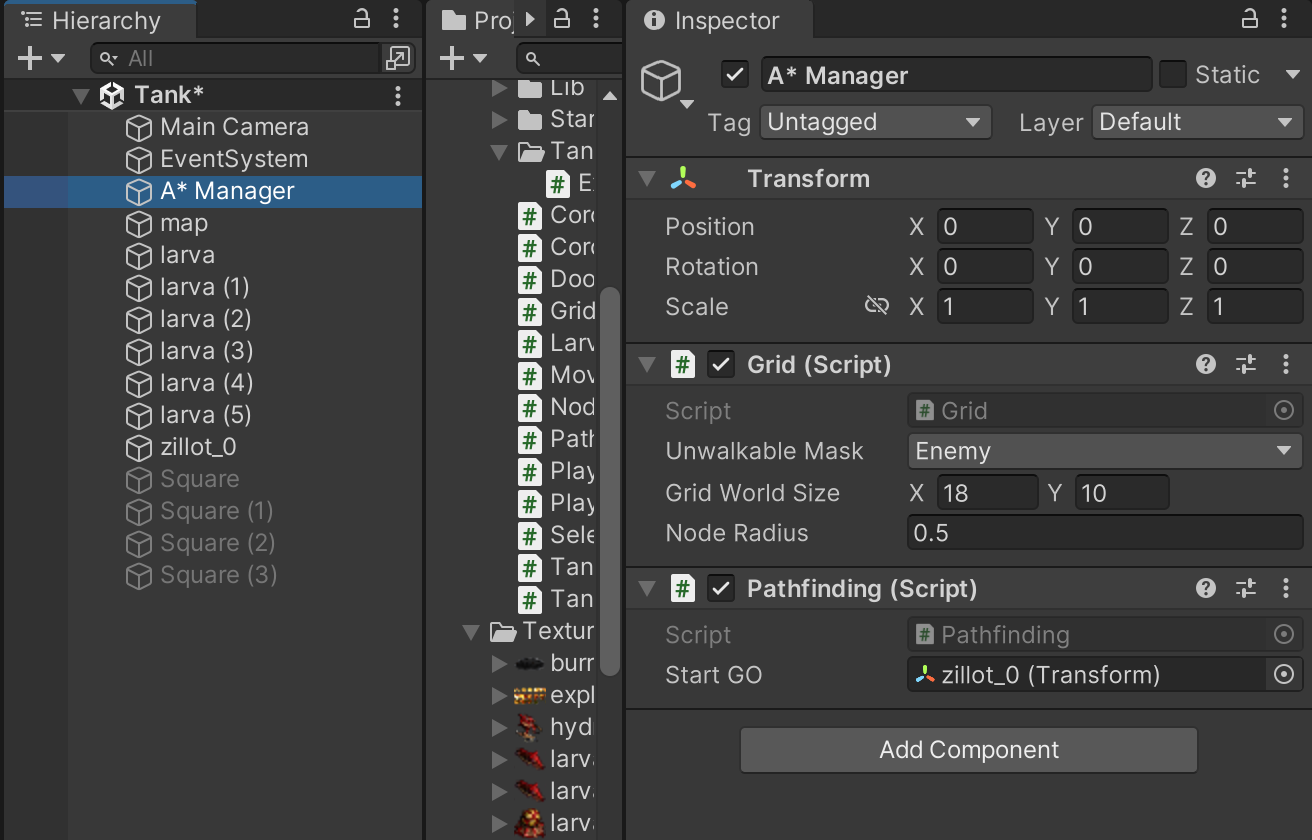
A* Manager에 Pathfinding 스크립트를 추가하고
Instpector에서 StartGo에 시작점인 Zillot을 넣는다.
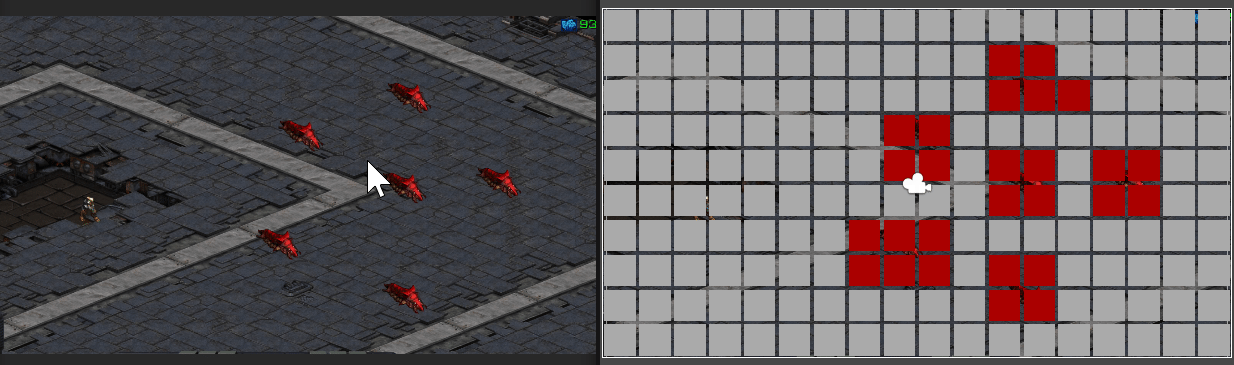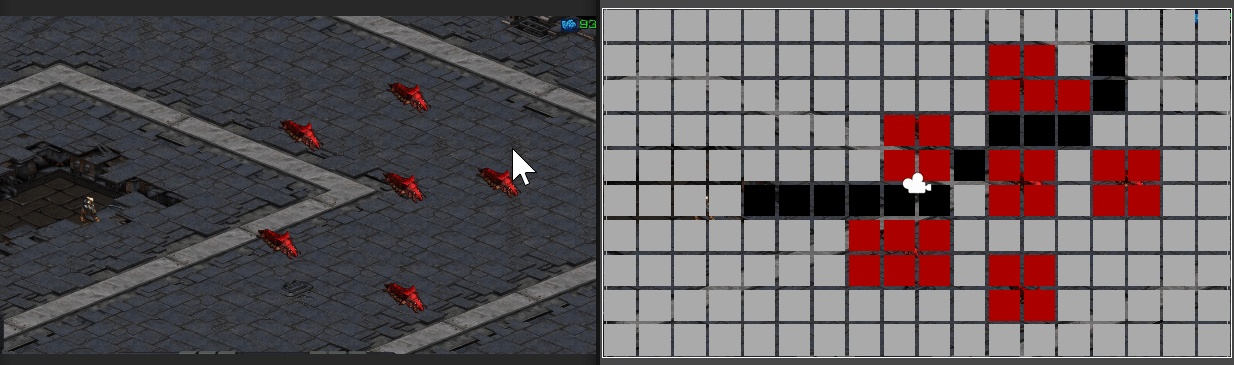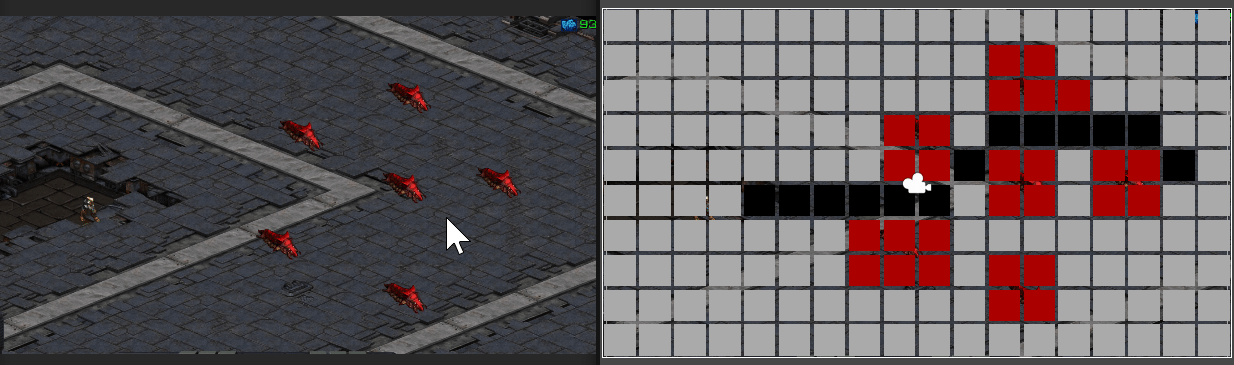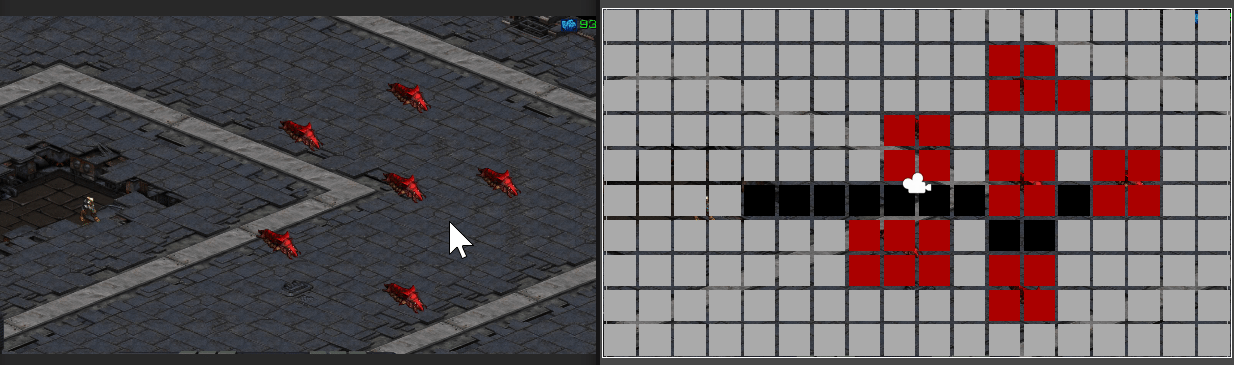
마우스 클릭 지점에 따라 경로가 표시되는 모습
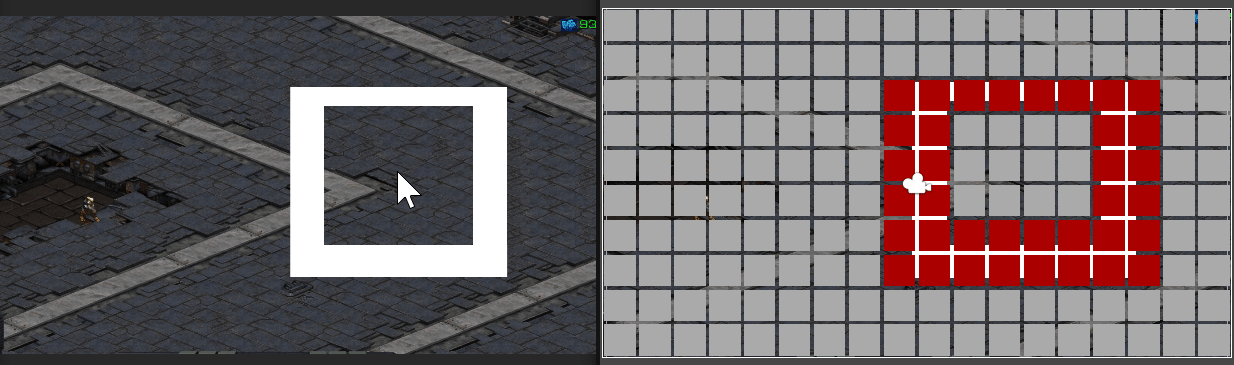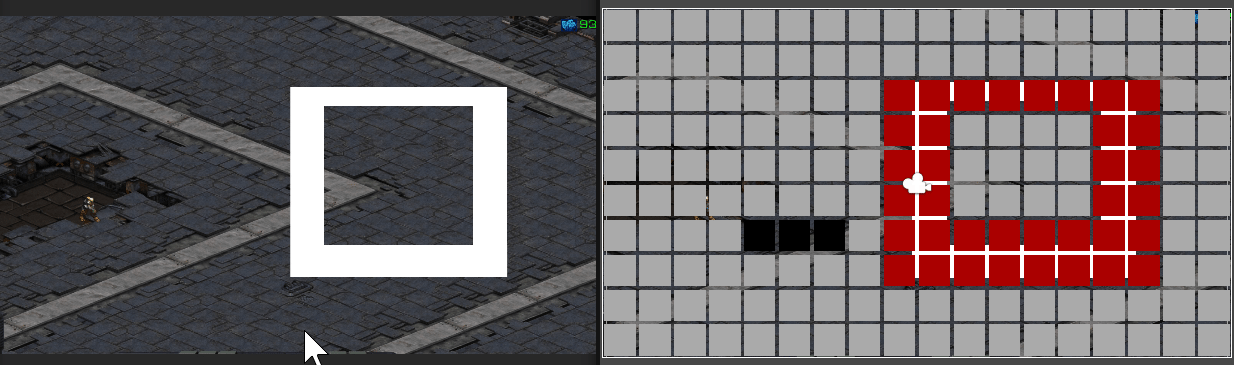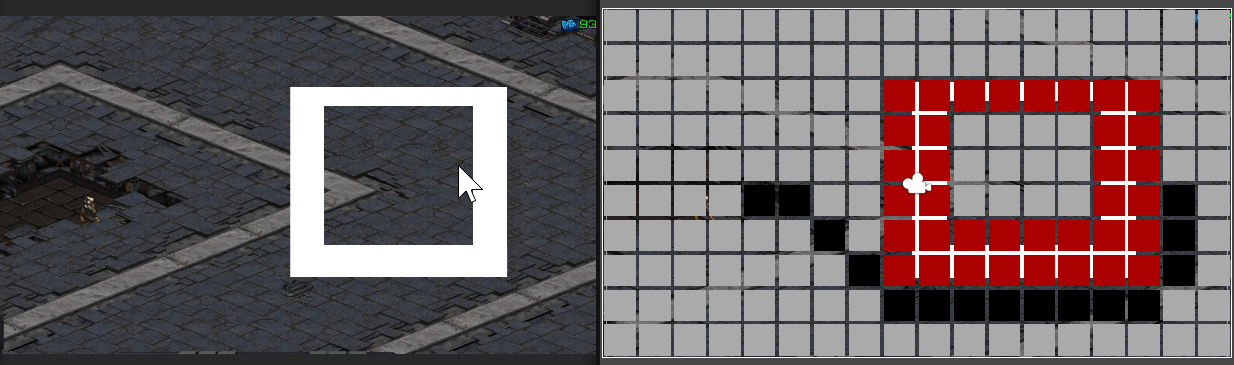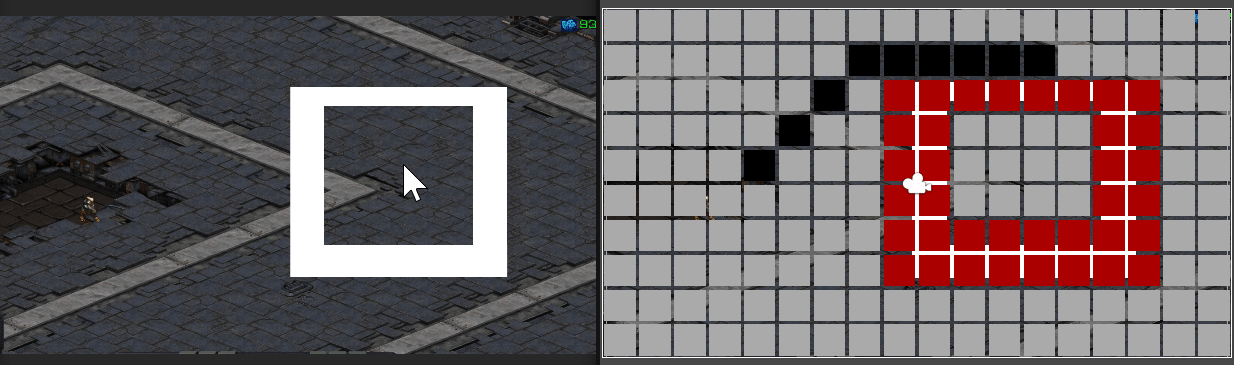
만약 길이 막혀 갈 수 없다면
경로 계산 및 경로가 그려지지 않는다.
'산대특 > 게임 플랫폼 응용 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Bullet 발사 시에 오브젝트 풀링으로 Bullet 관리하기 (0) | 2024.03.04 |
|---|---|
| A* 알고리즘 구현해보기 (3) - 구해진 경로를 따라 오브젝트 이동 시켜보기 (0) | 2024.03.04 |
| A* 알고리즘 구현해보기 (1) - 이동 불가 노드와 이동 가능 노드 구별하기 (0) | 2024.03.03 |
| Larva 클릭 및 드래그로 TargetPoint 지정하기 (0) | 2024.03.01 |
| 화면을 클릭할때까지 기다리다가 2초마다 "대기중" 이라고 출력하고, 화면을 클릭하면 "완료" 라고 출력하기 (0) | 2024.02.29 |